Group 4: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
\label{dim_eq2} | \label{dim_eq2} | ||
(M+m)\ddot X+B\dot X = -ml\frac{d^2}{dt^2}(\sin\phi_1+\sin\phi_2+ ... +\sin\phi_N) | (M+m)\ddot X+B\dot X = -ml\frac{d^2}{dt^2}(\sin\phi_1+\sin\phi_2+ ... +\sin\phi_N) | ||
\end{equation} where $\ | \end{equation} where $\phi_j$ is the angular displacement of the jth pendulum, $b$ is the pivot damping | ||
coefficient, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity, $l$ is the pendulum length, $X$ is the linear | coefficient, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity, $l$ is the pendulum length, $X$ is the linear | ||
displacement of the platform, $F$ is the impulsive drive, $M$ is the platform mass, $m$ is the metronome | displacement of the platform, $F$ is the impulsive drive, $M$ is the platform mass, $m$ is the metronome | ||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
\begin{equation} | \begin{equation} | ||
\label{nondim_param1} | \label{nondim_param1} | ||
\tau=t\sqrt\frac{g}{l} | \tau=t\sqrt{\frac{g}{l}} | ||
\end{equation} | \end{equation} | ||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
\begin{equation} | \begin{equation} | ||
\label{nondim_param3} | \label{nondim_param3} | ||
\tilde\gamma=b\sqrt\frac{l}{4g} | \tilde\gamma=b\sqrt{\frac{l}{4g}} | ||
\end{equation} | \end{equation} | ||
\begin{equation} | \begin{equation} | ||
\label{nondim_param4} | \label{nondim_param4} | ||
\Gamma=\frac | \Gamma=\frac{B}{(M+Nm)}\sqrt{\frac{l}{4g}} | ||
\end{equation} | \end{equation} | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
With a complete theoretical model, we must estimate the values of our parameters before we can fully construct a computer simulation of the experiment. | With a complete theoretical model, we must estimate the values of our parameters before we can fully construct a computer simulation of the experiment. | ||
== Parameters == | |||
Several parameters must be estimated for use in the simulation. With the exception of gravitational acceleration and the number of metronomes, all parameters must be estimated with a varying amount of uncertainty. The platform mass contains perhaps the least uncertainty, and is given (in kilograms) by $M=0.0655+N(0.094-m)$, where we include the mass of the metronome minus the bob in the total. The pendulum bob mass is estimated as $0.022kg$; this is only estimated because an exact measurement would require the destruction of borrowed experimental materials. | |||
The pivot damping coefficient, b, is estimated from a measurement of the decay time for an undriven oscillation of the metronome, experimentally determined as $t_{decay}=20 s$; the value used for b is thus $b=2m/t_{decay}=0.0022$. The platform damping coefficient, B, has a considerable amount of uncertainty; we expect that for our soda cans rolling on a smooth surface, the damping should be very small, so we somewhat arbitrarily pick $B=0.001$. | |||
As far as the parameters corresponding to the modeling of the escapement mechanism are concerned, $\gamma$ is difficult to estimate, but $c$ can be predicted fairly well. For $c$, this is because it is primarily the magnitude of this kick that determines the amplitude of the pendula after several oscillations; we experimentally observe oscillations in the range of about $45^{\circ}$, so we can adjust the value of $c$ accordingly. For our simulation, we have decided to use $\gamma=0.97$ and $c=0.025$, as was used in Wiesenfeld and Borrero-Echeverry\cite{Borrero}. | |||
The pendulum length l, the final remaining parameter, is difficult to estimate because of a simplification in the model, different from the metronome we use in our experiment. The simulation models a pendulum with a point mass, $m$, a distance $l$ from the pivot. The metronome, in reality, has two spatially extended masses located at two different distances from the pivot. An attempt to calculate an equivalent distance resulted in $l=0.025 m$; however, this gives a natural frequency for the simulation that is considerably higher than what is experimentally observed. The simulation was run a second time with a new value of $l=0.1m$ to match the natural frequency of the pendula in the simulation to that of the experiment. | |||
Revision as of 01:26, 16 December 2011
Group Members: Luis Jover, Vlad Levenfeld, Brad Taylor, & Jeff Tithof
We plan to numerically and experimentally investigate the occurrence of and timescale for synchronization of up to $N=10$ coupled metronomes.
Background
The phenomenon of synchronization is found throughout nature and in many applications of different fields of science. Examples of synchronization include the flashing of firefly populations, the firing of pacemaker cells in the heart, applications of Josephson junctions, coupled fiber laser arrays, and perhaps even epileptic seizures. Many instances of synchronization in nature and applications in science become extremely complicated as soon as multiple variables or several coupled oscillators are introduced. However, the pervasive presence of synchronization in nature and science motivates work towards a deep understanding of such phenomena. So, as with any system that is to be scientifically understood, the simplest case is the best place to begin; for synchronization, the case of two identical, coupled oscillators is perhaps the simplest.
Research into the mutual synchonization of two identical coupled oscillators is believed to date back to the work of Christiaan Huygens in the 1600's, in which he discovered and investigated the synchronization of two pendulum clocks hanging on a common support beam. Although his goal was to solve the "Longitude Problem" at the time, he did reach some insightful conclusions about the nature of this system, eventually concluding that small movements of the support beam with every oscillation were responsible for the antiphase synchronization that consistently occurred.
Significant progress has been made in explaining simple instances of synchronization. In 2002, Bennett et al. <ref>M. Bennett, M. F. Schatz, H. Rockwood, and K. Wiesenfeld, ``Huygens's clocks," Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 458, 563-579 (2002).</ref> constructed an apparatus meant to recreate the setup decribed by Christiaan Huygens. The experimental and numerical results agree qualitatively with records from Huygens's research. Concurrently, Pantaleone <ref>J. Pantaleone, ``Synchronization of metronomes," American Journal of Physics 70, 992-1000 (2002).</ref> investigated a similar setup in which metronomes were placed on a common support which was free to roll across cylinders, allowing coupling through the low-friction horizontal translation of the platform. Pantaleone's theoretical analysis provided agrees with the experimental observations reported.
In 2009, Ulrichs et al. <ref>H. Ulrichs, A. Mann, and U. Parlitz, ``Synchronization and chaotic dynamics of coupled mechanical metronomes," Chaos 19, 043120 (2009).</ref> reported agreement with Pantaleone's results in computer simulations. Additionally, these simulations were run for coupling of up to 100 metronomes and reportedly showed chaotic and hyperchaotic behavior. A paper by Borrero-Echeverry and Wiesenfeld <ref>Daniel Borrero-Echeverry and Kurt Wiesenfeld, ``Huygens (and Others) Revisted," Publication in progress, Obtained through personal contact (2011).</ref>, currently in the process of publication, describes a theoretical model which encompasses the behavior of both types of oscillators often studied, clocks and metronomes, which often contrast in the phase of synchronization encountered. This paper attributes the difference in synchronization phase to differences in parameters of the oscillators.
An arguably strong theoretical understanding of the $N=2$ case has been developed in recent years; it seems appropriate to expand this theory to a larger number of coupled oscillators. This is the goal of the current proposal.
Experiment
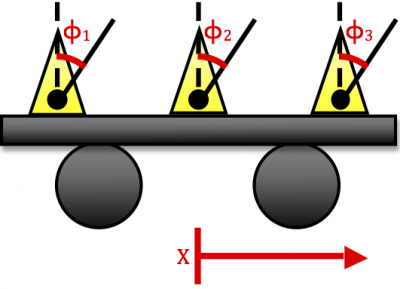
The figure to the right shows the experimental setup for the case of $N=3$. $N$ metronomes will be started with ``random" initial conditions and then placed on a rigid supporting platform, which will then be placed on top of two cylinders, allowing free horizontal translation. The translation of this platform is what provides the coupling between oscillators. Data will be collected through imaging the oscillations with a webcam and extracting the positions of each metronome as a function of time. A MATLAB script will quantitatively compare the phases and determine synchonization by criteria similar to that above. The occurrence, characteristics, and associated timescales for any synchronization encountered will be recorded. Experimental results will be compared to numerical results.
Below is a video of synchronization for $N=5$ from YouTube. <videoflash>Aaxw4zbULMs</videoflash>
Theory
The equations of motion for two coupled pendulums are available in Bennett et al.\cite{Bennett} and Wiesenfeld and Borrero-Echeverry\cite{Borrero}. These equations may easily be extended to $N$ metronomes:
\begin{equation} \label{dim_eq1} \ddot\phi_j+b\dot\phi_j+\frac{g}{l}\sin\phi_j=-\frac{1}{l}\ddot X \cos\phi_j+F_j \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \label{dim_eq2} (M+m)\ddot X+B\dot X = -ml\frac{d^2}{dt^2}(\sin\phi_1+\sin\phi_2+ ... +\sin\phi_N) \end{equation} where $\phi_j$ is the angular displacement of the jth pendulum, $b$ is the pivot damping coefficient, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity, $l$ is the pendulum length, $X$ is the linear displacement of the platform, $F$ is the impulsive drive, $M$ is the platform mass, $m$ is the metronome rod mass, $B$ is the platform friction coefficient, and the dots represent differentiation with respect to time.
Nondimensionalizing results in the following:
\begin{equation} \label{nondim_eq1} \frac{d^2\phi_j}{{d\tau}^2}+2\tilde\gamma\frac{d\phi_j}{d\tau}+\sin\phi_j=-\frac{d^2Y}{{d\tau}^2}\cos\phi_j+\tilde F_j \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \label{nondim_eq2} \frac{d^2Y}{{d\tau}^2}+2\Gamma\frac{dY}{d\tau}=-\mu\frac{d^2}{d\tau^2}(\sin\phi_1+...+\sin\phi_N) \end{equation}
where we have introduced the dimensionless parameters:
\begin{equation} \label{nondim_param1} \tau=t\sqrt{\frac{g}{l}} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \label{nondim_param2} \mu=\frac{m}{M+Nm} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \label{nondim_param3} \tilde\gamma=b\sqrt{\frac{l}{4g}} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \label{nondim_param4} \Gamma=\frac{B}{(M+Nm)}\sqrt{\frac{l}{4g}} \end{equation}
All parameters and variables described are well defined and may be experimentally measured, with the exception of $\tilde{F_j}$, the impulsive drive of the metronome, which receives a treatment first described in [1]. The escapement mechanism which ``kicks" the metronome is mimicked in two parts: first, the angular velocity of the pendulum is slowed by some factor $\gamma$, and then, a numerical constant $c$ is added to the angular velocity:
\begin{equation} \label{kick} \left|\frac{d\phi}{d\tau}\right|\to\gamma\left|\frac{d\phi}{d\tau}\right|+c \end{equation}
With a complete theoretical model, we must estimate the values of our parameters before we can fully construct a computer simulation of the experiment.
Parameters
Several parameters must be estimated for use in the simulation. With the exception of gravitational acceleration and the number of metronomes, all parameters must be estimated with a varying amount of uncertainty. The platform mass contains perhaps the least uncertainty, and is given (in kilograms) by $M=0.0655+N(0.094-m)$, where we include the mass of the metronome minus the bob in the total. The pendulum bob mass is estimated as $0.022kg$; this is only estimated because an exact measurement would require the destruction of borrowed experimental materials.
The pivot damping coefficient, b, is estimated from a measurement of the decay time for an undriven oscillation of the metronome, experimentally determined as $t_{decay}=20 s$; the value used for b is thus $b=2m/t_{decay}=0.0022$. The platform damping coefficient, B, has a considerable amount of uncertainty; we expect that for our soda cans rolling on a smooth surface, the damping should be very small, so we somewhat arbitrarily pick $B=0.001$.
As far as the parameters corresponding to the modeling of the escapement mechanism are concerned, $\gamma$ is difficult to estimate, but $c$ can be predicted fairly well. For $c$, this is because it is primarily the magnitude of this kick that determines the amplitude of the pendula after several oscillations; we experimentally observe oscillations in the range of about $45^{\circ}$, so we can adjust the value of $c$ accordingly. For our simulation, we have decided to use $\gamma=0.97$ and $c=0.025$, as was used in Wiesenfeld and Borrero-Echeverry\cite{Borrero}.
The pendulum length l, the final remaining parameter, is difficult to estimate because of a simplification in the model, different from the metronome we use in our experiment. The simulation models a pendulum with a point mass, $m$, a distance $l$ from the pivot. The metronome, in reality, has two spatially extended masses located at two different distances from the pivot. An attempt to calculate an equivalent distance resulted in $l=0.025 m$; however, this gives a natural frequency for the simulation that is considerably higher than what is experimentally observed. The simulation was run a second time with a new value of $l=0.1m$ to match the natural frequency of the pendula in the simulation to that of the experiment.
References
<references />